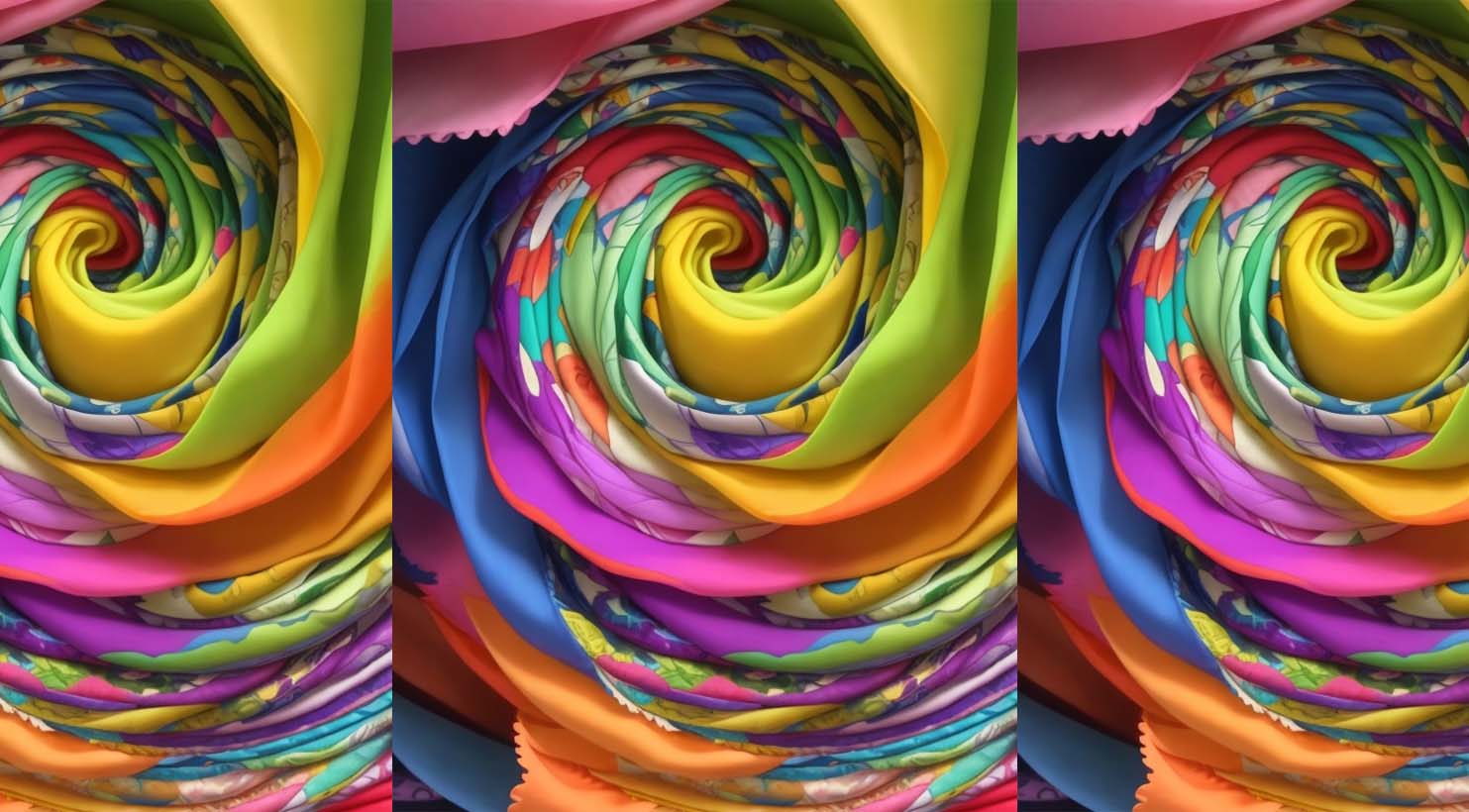
Color properties refer to the characteristics that describe a color and how it appears to the human eye. These properties help us understand and differentiate between colors. The three primary color properties are:
1. Hue:
– Hue is often used interchangeably with the term “color” itself.
– It refers to the attribute that allows us to distinguish red from blue or green from yellow.
– Hue is determined by the dominant wavelength of light that a color reflects or emits.
– In the color wheel, different hues are represented as distinct points around the circle. For example – red, blue, and yellow (green) are primary hues.
2. Saturation (Chroma):
– Saturation, also known as chroma or intensity, measures the vividness or purity of a color.
– Highly saturated colors are vivid and appear pure, while desaturated colors are muted or faded.
– Lowering the saturation of a color by adding gray or complementary colors makes it less intense.
– Saturation affects the strength and vibrancy of a color.
3. Value (Lightness/Darkness):
– It is often described as a color’s relative brightness.
– In the context of color properties, value is independent of hue and saturation.
– Manipulating value is essential for creating contrast and defining the form and structure of objects in art and design.
These color properties are fundamental in understanding and working with colors in various fields, such as art, design, and photography. By adjusting and balancing these properties, artists and designers can create visually appealing and harmonious compositions while conveying specific moods and emotions.